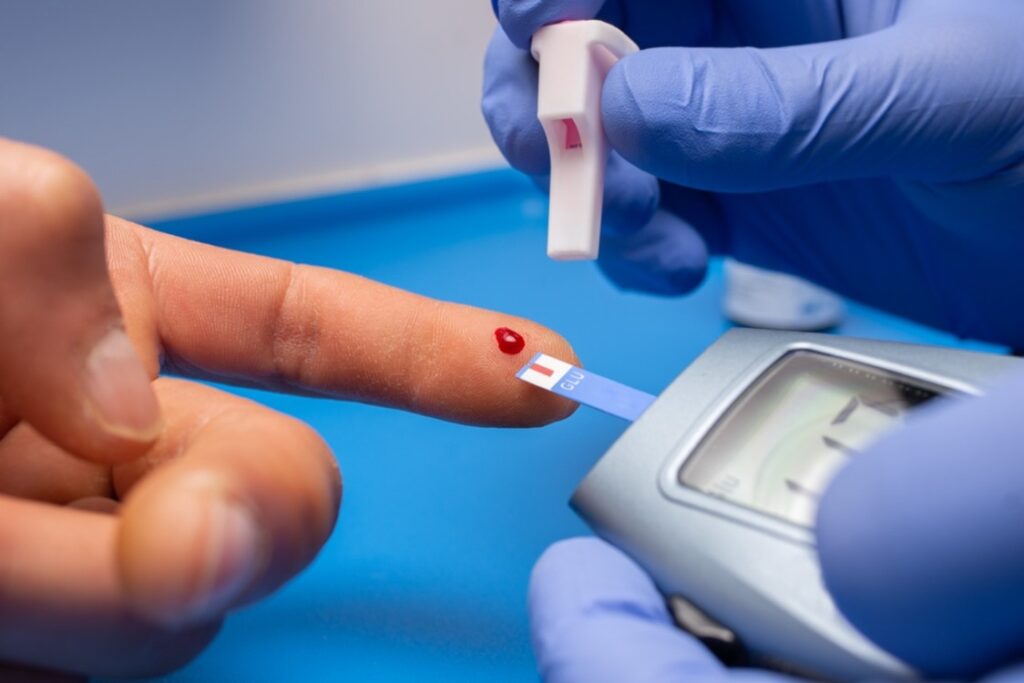
Type 2 diabetes is a common health condition where the body struggles to effectively use insulin, a hormone vital for regulating blood sugar levels. Unlike Type 1 diabetes, which is usually diagnosed early in life and involves the body’s inability to produce insulin, Type 2 often develops over time and is linked to lifestyle factors.
Understanding type 2 diabetes is the first step in taking control, and this guide is designed to do just that, in simple, easy-to-understand terms.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
· Insulin and Your Body: In type 2 diabetes, your body either resists the effects of insulin (a hormone regulating the movement of sugar into your cells) or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels.
· Symptoms: These can include increased thirst, frequent urination, hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow-healing sores.
Managing Type 2 Diabetes
· Healthy Eating: Focus on fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains. Limit foods high in sugar and fat.
· Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
· Monitor Your Blood Sugar: Keep track of your blood sugar levels as recommended by your healthcare provider.
Treatment Options
· Medications: Many people need medication to manage their diabetes. Metformin is often the first medication prescribed.
· Insulin Therapy: Some people with type 2 diabetes may also need insulin therapy at some point.
The Power of Lifestyle Changes
· Weight Loss: Losing 5% to 10% of your total weight can significantly improve blood sugar control.
· Stop Smoking and Limit Alcohol: Smoking increases the risk of type 2 diabetes complications. Limit alcohol or avoid it.
Preventing Complications
· Regular Check-ups: Regular visits with your healthcare provider are essential to monitor and manage your condition.
· Eye Exams: Diabetes can lead to eye problems. Regular eye checks are important.
Advancements in Insulin Therapy:
· Ultra-Long-Acting Insulins: These new insulins have a steadier rate of action and lower risk of hypoglycemia.
· Inhaled Insulin: Offering an alternative to injections for mealtime blood sugar control.
Conclusion
Living with type 2 diabetes requires ongoing care and lifestyle adjustments, but it doesn’t have to take over your life. With the right strategies and support, you can manage your diabetes and lead a full, healthy life. Remember, every small step counts in your journey to a healthier you.